Detailed Introduction
Exothermic welding is a type of exothermic fusion welding that utilizes the extremely high heat generated during a chemical exothermic reaction to complete the fusion. It is also known as: fire-mud welding, exothermic fusion welding, exothermic welding, thermochemical welding, etc. The exothermic chemical reaction is very fast, completing the welding in just a few seconds. The extremely high heat generated is effectively conducted to the fusion point, fusing them into a single molecular bond. It requires no other heat energy and is used for connecting metal conductors in grounding circuits.
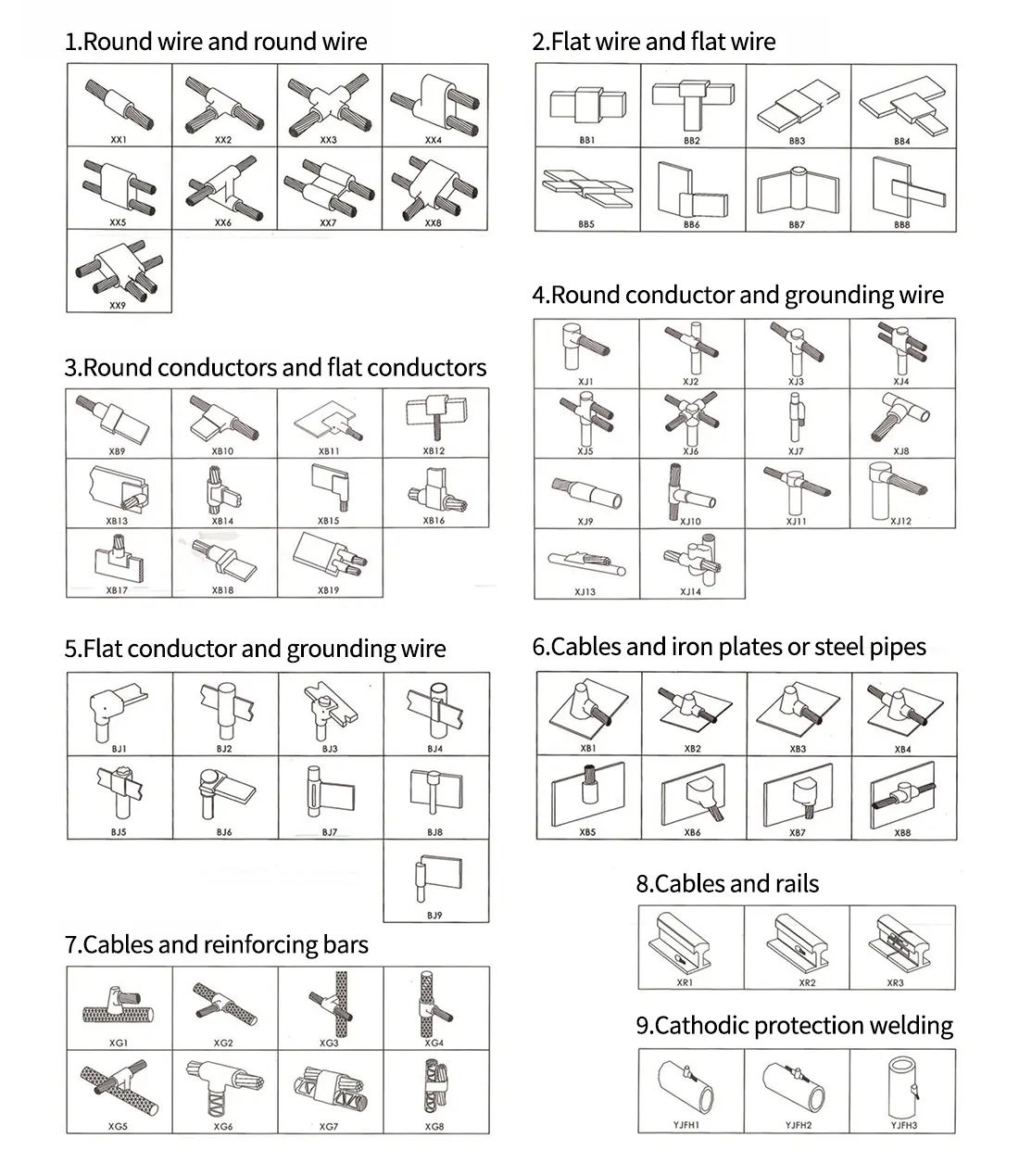
Exothermic welding can mainly weld pure copper, brass, bronze, red copper, copper-clad steel, pure iron, stainless steel, and other metal materials. Welding includes different connection methods, such as butt joints, cross joints, parallel connections, T-joints, etc.
Exothermic welding is widely used for welding lightning protection grounding, anti-static grounding, protective grounding, and working grounding in power plants, substations, transmission line towers, communication base stations, airports, railways, various high-rise buildings, microwave relay stations, network computer rooms, petrochemical plants, oil depots, and other places.
Exothermic Welding Method
Step 1: Clean the exothermic welding mold. Remove moisture from the mold using heating. Then, place the cleaned metal conductor into the mold and clamp it tightly to ensure there are no gaps.
Step 2: Place the metal spacer at the bottom of the reaction chamber of the exothermic welding mold.
Step 3: Pour the welding powder into the reaction chamber, leaving some ignition powder on the mold lip.
Step 4: Cover the exothermic welding mold and ignite the ignition powder on the mold lip with an ignition gun.
Step 5: The reaction proceeds until the molten metal completely solidifies.
Step 6: Open the exothermic welding mold and clean it for future use. A complete exothermic welded connector is now manufactured.